Kanban, a method for managing knowledge work with an emphasis on just-in-time delivery and workflow efficiency, has revolutionized how teams and organizations operate. Originating from Japan, the Kanban methodology has become a cornerstone in various industries, particularly in software development and manufacturing. This article explores what Kanban is, how it works, and its history.
What is Kanban?
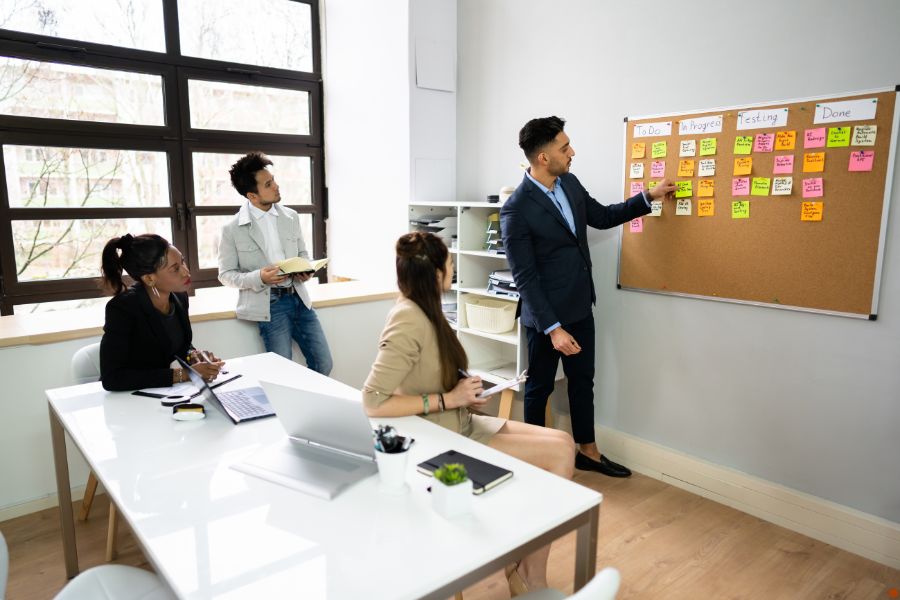
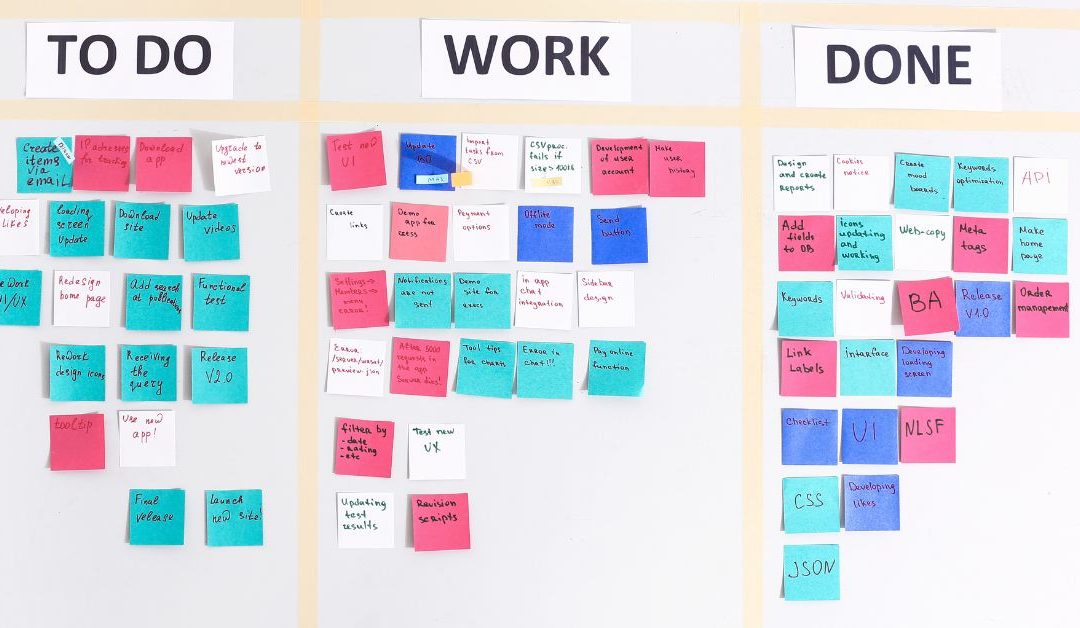
Kanban is a visual system for managing work as it moves through a process. It helps visualize work, maximize efficiency, and improve continuously. The method involves a Kanban board, which is a tool used to visualize the workflow and includes columns representing different stages of the process. Tasks, represented as cards, move from one column to another as they progress through various stages, from “To Do” to “Done.”
How Does Kanban Work?
- Visualizing the Workflow:
- The first step in Kanban is to map out the workflow. This involves creating a Kanban board that includes columns representing different stages of work. For example, a software development team might have columns like “Backlog,” “In Progress,” “Testing,” and “Completed.”
- Limiting Work in Progress (WIP):
- One of the key principles of Kanban is to limit the amount of work in progress. This helps to prevent overloading the team and ensures that work is completed efficiently. For instance, a WIP limit might restrict the “In Progress” column to only three tasks at a time.
- Managing Flow:
- The goal is to optimize the flow of tasks from one stage to another. By visualizing the workflow and setting WIP limits, teams can identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. This continuous monitoring helps in maintaining a steady flow of work.
- Making Process Policies Explicit:
- Clearly defined rules and policies guide the team on how to handle tasks. This could include criteria for moving tasks between columns or defining what constitutes a “completed” task.
- Implementing Feedback Loops:
- Regular meetings and reviews are essential in Kanban to assess performance and identify areas for improvement. These feedback loops help in refining the process and making data-driven decisions.
- Improving Collaboratively:
- Kanban promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Teams are encouraged to make incremental changes to the process, which leads to better efficiency and productivity.
History and Origin of Kanban
Kanban originated in Japan, developed by Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, to improve manufacturing efficiency. The term “Kanban” itself means “signboard” or “billboard” in Japanese. The method was initially used as a scheduling system for lean manufacturing, helping Toyota to optimize production and inventory levels.
The concept gained global recognition and was later adapted for use in knowledge work, particularly in software development. The Agile movement embraced Kanban as a method to visualize work, limit work in progress, and optimize flow. Today, Kanban is widely used across various industries, from IT and finance to healthcare and education.
Benefits of Kanban
- Enhanced Visibility:
- The visual nature of Kanban makes it easy to see the status of work at a glance, facilitating better communication and transparency.
- Increased Efficiency:
- By limiting work in progress and managing flow, Kanban helps teams focus on completing tasks rather than starting new ones, thereby improving overall efficiency.
- Flexibility:
- Unlike other methodologies, Kanban does not prescribe specific roles or processes, making it adaptable to various industries and workflows.
- Continuous Improvement:
- The emphasis on feedback loops and collaborative improvement ensures that the team is always striving for better ways to work.
- Reduced Waste:
- Kanban helps in identifying and eliminating wasteful activities, leading to a more streamlined and cost-effective process.
Conclusion
Kanban is a versatile and powerful tool for managing work, whether in manufacturing, software development, or other industries. Its principles of visualizing work, limiting work in progress, and optimizing flow make it an effective method for improving efficiency and productivity. With its roots in the lean manufacturing practices of Toyota, Kanban has evolved into a comprehensive methodology that continues to shape how modern organizations operate. As we move towards a more complex and fast-paced world, Kanban’s emphasis on continuous improvement and adaptability makes it an invaluable tool for any team or organization.